Abstract
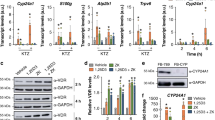
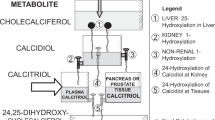
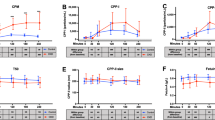
THE discovery that vitamin D must first be converted into the metabolites 25-hydroxycholecalciferol1 (25 OH-D3) and 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol2 (1,25(OH)2-D3) before calcium absorption across the small intestine is enhanced has radically changed existing ideas as to the mode of action of vitamin D. Indeed, it is now well established that the most active metabolite of vitamin D for calcium absorption, 1,25(OH)2-D3, is produced solely by the kidney3 and that its production and secretion are under very fine endocrine control. This finding, together with the observation that 1,25(OH)2-D3 is specifically located in the nucleus of the target cell4 and the apparent involvement of RNA and protein synthesis5–7 in the intestinal action of vitamin D, provide the basis of the proposal that 1,25(OH)2-D3 can be classed as a steroid hormone.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blunt, J. W., DeLuca, H. F., and Schnoes, H. D., Biochemistry N.Y., 7, 3317 (1968).
Lawson, D. E. M., Fraser, D. R., Kodicek, E., Morris, H. R., and Williams, D. H., Nature, 230, 228 (1971).
Fraser, D. R., and Kodicek, E., Nature, 228, 764 (1970).
Lawson, D. E. M., Wilson, P. W., and Kodicek, E., Nature, 222, 171 (1969).
Zull, J. E., Czarnowska-Misztal, E., and DeLuca, H. F., Science, N.Y., 149, 182 (1965).
Norman, A. W., Science, N.Y., 149, 184 (1965).
Lawson, D. E. M., Wilson, P. W., Barker, D. C., and Kodicek, E., Biochem. J., 115, 263 (1969).
Corradino, R. A., Nature, 243, 41 (1973).
Wasserman, R. H., Corradino, R. A., and Taylor, A. N., J. biol. Chem., 243, 3978 (1968).
Drescher, D., and DeLuca, H. F., Biochemistry, N.Y., 10, 2308 (1971).
Lawson, D. E. M., and Emtage, J. S., in The Metabolism and Function of Vitamin D (Biochemical Society, London, in the press).
Palmiter, R. D., J. biol. Chem., 248, 2095 (1973).
Neuberger, A., and Marshal, R. D., in Glycoproteins (edit. by Gottschalk, A.), 5, 299 (BBA Library, Elsevier, New York, 1966).
Palmiter, R. D., Palacios, R., and Schimke, R. T., J. biol. Chem., 247, 3296 (1972).
Mans, R. J., and Novelli, G. D., Archs Biochem. Biophys., 94, 48 (1961).
Darnbrough, C., Legon, S., Hunt, T., and Jackson, R. J., J. molec. Biol., 76, 379 (1973).
Jackson, R. J., and Hunter, A. R., Nature, 227, 672 (1970).
Palmiter, R. D., Oka, T., and Schimke, R. T., J. biol. Chem., 246, 724 (1971).
Laemmli, U. K., Nature, 227, 680 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EMTAGE, J., LAWSON, D. & KODICEK, E. Vitamin D-induced Synthesis of mRNA for Calcium-binding Protein. Nature 246, 100–101 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1038/246100a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/246100a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.