Abstract
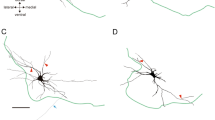
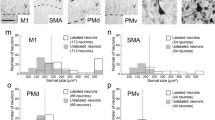
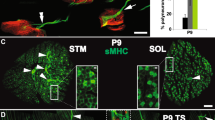
Cerf and Chacko1 found that the number and diameter of motor neurone dendrites decreased after axotomy in the adult bullfrog. The purposes of the investigation reported here are to confirm and extend these observations in a mammal, to determine whether the dendritic changes are due to loss of axoplasm or loss of effective neuromuscular transmission, to see if dendrites recover after nerve regeneration has restored contact between the nerve and the originally innervated muscle mass, and if they recover after the regenerating nerve makes contact with different denervated muscle. Quantitative assessments of the dendritic spread of developing rat and human cortical neurones have been made by Eayrs and Goodhead2, and Schadé and van Groenigen3. Schapiro and Vukovitch4 found that the number of dendritic spines of rat cortical neurones could be influenced by variety of experience during development; Jones and Thomas5 and Matthews and Powell6 reported a decrease in the number and length of dendrites after deafferentation. Possible neuronal plasticity in the central nervous system of adult rats has been reported by Raisman7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cerf, J. A., and Chacko, L. W., J. Comp. Neurol., 109, 205 (1958).
Eayrs, J. T., and Goodhead, B., J. Anat., 93, 385 (1959).
Schadé, J. P., and Van Groenigen, W. B., Acta Anat., 47, 74 (1961).
Schapiro, S., and Vukovitch, K. A., Science, 167, 292 (1970).
Jones, W. H., and Thomas, D. B., J. Anat., 96, 375 (1962).
Matthews, M. R., and Powell, T. P. S., J. Anat., 96, 89 (1962).
Raisman, G., Brain Res., 14, 25 (1969).
Sholl, D. A., J. Anat., 87, 387 (1953).
Watson, W. E., J. Physiol., 180, 741 (1965).
Watson, W. E., J. Physiol., 202, 611 (1969).
Watson, W. E., J. Physiol., 210, 321 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SUMNER, B., WATSON, W. Retraction and Expansion of the Dendritic Tree of Motor Neurones of Adult Rats induced in vivo. Nature 233, 273–275 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/233273a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/233273a0
This article is cited by
-
Reduced cholinergic and glutamatergic synaptic input to regenerated motoneurons after facial nerve repair in rats: potential implications for recovery of motor function
Brain Structure and Function (2014)
-
Manual stimulation of forearm muscles does not improve recovery of motor function after injury to a mixed peripheral nerve
Experimental Brain Research (2008)
-
Choline acetyltransferase and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in motoneurons after different types of nerve injury
Journal of Neurocytology (1993)
-
The effect of axon injury on microtubule-associated proteins MAP2, 3 and 5 in the hypoglossal nucleus of the adult rat
Journal of Neurocytology (1992)
-
Characterization of the sprouting response of axon-like processes from retinal ganglion cells after axotomy in adult hamsters: a model using intravitreal implantation of a peripheral nerve
Journal of Neurocytology (1992)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.