Abstract
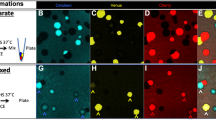
IN the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans, strains with a chromosome segment in duplicate (one in normal position, one translocated to another linkage group) are unstable at mitosis1,2. This “mitotic non-conformity” is provoked by chromosomal imbalance and initial changes of genotype are confined largely to the segments carried in duplicate3,4. Duplication strains, which have a characteristic morphology and reduced linear growth rate, give sectors produced by nuclei which have undergone spontaneous deletions, of variable size, from one or other duplicate segment. Sectors can almost always be scored unequivocally by their improved morphology and relative growth advantage, determined by nuclei more nearly haploid in quantity than those of the duplication parent. In suitably marked strains, loss of one or more dominant alleles gives sectors differing from the parent in conidial colour and/or nutritional requirements (Fig. 1a). The approximate size of each deletion, and the segment involved, can be determined by genetic analysis or sometimes simply by the morphology, nutritional requirements and stability or instability of the sector carrying it. This system seems to offer a simple screening test for deletion-producing agents and for any selective activity they might show towards particular chromosome regions. In addition, success in modifying sector frequency might help in elucidating the processes of mitotic non-conformity. The first attempt to induce deletions, using trypan blue (TB), has been successful.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bainbridge, B. W., and Roper, J. A., J. Gen. Microbiol., 42, 417 (1966).
Nga, B. H., and Roper, J. A., Genetics, 58, 193 (1968).
Nga, B. H., and Roper, J. A., Genet. Res., 14, 63 (1969).
Roper, J. A., and Nga, B. H., Genet. Res., 14, 127 (1969).
Pontecorvo, G., Roper, J. A., Hemmons, L. M., Macdonald, K. D., and Bufton, A. W. J., Adv. Genet., 5, 141 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COOKE, P., ROPER, J. & WATMOUGH, W. Trypan Blue-induced Deletions in Duplication Strains of Aspergillus nidulans. Nature 226, 276–277 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/226276a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/226276a0
This article is cited by
-
Effects of ethidium bromide in diploid and duplication strains of Aspergillus nidulans
Experientia (1977)
-
Mitotic non-conformity in Aspergillus nidulans: the effects of caffeine
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1972)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.