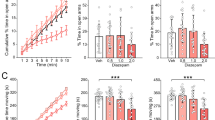
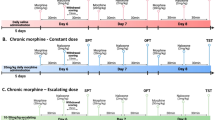
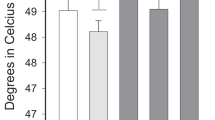
Abstract
THE narcotic analgesics and their antagonists form a series ranging from morphine, which is a powerful and highly addictive analgesic, to naloxone, which is a potent antagonist of morphine1. One of the drugs between these extremes is pentazocine, which has both analgesic and antimorphine properties. In man, pentazocine is an effective analgesic drug; but, unlike the narcotic analgesics, it does not support morphine dependence and it precipitates abstinence effects in persons dependent on morphine2. Unlike cyclazocine and nalorphine, pentazocine rarely causes hallucinations in man. These properties render pentazocine a useful analgesic of a new type; but tests in animals that show its profile of activity are not well developed. For example, pentazocine is poorly effective in antinociceptive tests based on mechanical pressure, in which morphine and other narcotic analgesics are active; whereas in the antinociceptive tests in animals in which pentazocine has proved effective3–8, it cannot clearly be distinguished from other narcotic antagonists not useful as analgesics in man (cyclazocine, levallorphan and nalorphine) nor from antipyretic analgesics, such as aspirin and mefenamic acid. We describe here new tests in rodents that we have devised to indicate those features of the activity of pentazocine that are important for its clinical usefulness in man.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kosterlitz, H. W., and Watt, A. J., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 33, 266 (1968).
Fraser, H. F., and Harris, L. S., Ann. Rev. Pharmacol., 7, 277 (1967).
Taber, R. I., Greenhouse, D. D., and Irwin, S., Nature, 204, 189 (1964).
Blumberg, H., Wolf, P. S., and Dayton, H. B., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 118, 763 (1965).
Pearl, J., and Harris, L. S., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 154, 319 (1966).
Blane, G. F., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 19, 367 (1967).
Collier, H. O. J., Dinneen, L. C., Johnson, C. A., and Schneider, C., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 32, 295 (1968).
Helfer, H., and Jaques, R., Helv. Physiol. Acta, 26, 137 (1968).
Keele, C. A., and Armstrong, D., Substances Producing Pain and Itch (Arnold, London, 1964).
Finney, D. J., Statistical Method in Biological Assay, second ed. (Griffin, London, 1964).
Green, A. F., Young, P. A., and Godfrey, E. I., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 6, 572 (1951).
Collier, H. O. J., in Evaluation of Drug Activities: Pharmacometrics (edit. by Laurence, D. R., and Bacharach, A. L.), 183 (Academic Press, London and New York, 1964).
Bianchi, C., and Franceschini, J., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 9, 280 (1954).
Collier, H. O. J., Warner, B. T., and Skerry, R., Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother., 17, 28 (1961).
Straub, W., Deutsch. Med. Wschr., 37, 1462 (1911).
Shemano, I., and Wendel, H., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 6, 334 (1964).
Schneider, C., Nature, 220, 586 (1968).
Winder, C. V., Welford, M., Wax, J., and Kaump, D. H., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 154, 161 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COLLIER, H., SCHNEIDER, C. Profiles of Activity in Rodents of Some Narcotic and Narcotic Antagonist Drugs. Nature 224, 610–612 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/224610a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/224610a0
This article is cited by
-
[d-Pen2,d-Pen5]enkephalin, the standard delta opioid agonist, induces morphine-like behaviors in mice
Psychopharmacology (1990)
-
Effects of prostaglandins and other putative chemical intermediaries on the activity of canine testicular polymodal receptors studied in vitro
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1987)
-
Effects of morphine and chloropromazine on the detection of shock
Psychopharmacology (1978)
-
Comparison of withdrawal precipitating properties of various morphine antagonists and partial agonists in relation to their stereospecific binding to brain homogenates
Psychopharmacologia (1976)
-
Facilitation de r�actions nociceptives par la naloxone chez la souris et chez le rat
Psychopharmacologia (1974)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.