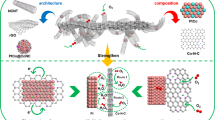
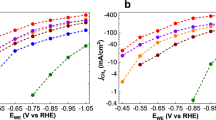
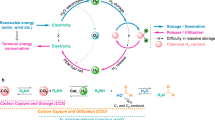
Abstract
A NUMBER of investigators have reported high-performance, direct hydrocarbon fuel cells1–4. In every case, the direct hydrocarbon anode has used a large amount of high-area platinum black or Raney platinum in the range of about 10–100 mg/cm2 of geometric electrode area. This tends to counteract the advantage of being able to operate on inexpensive hydrocarbon fuels. Furthermore, there is a tendency for performance to be proportional to platinum content. Niedrach5 has shown that ‘Teflon’-bonded electrodes6 containing mechanical mixtures of platinum black with tantalum or platinum deposited on tantalum give performance on propane which is just proportional to the platinum content. Thus, the advantage of reduction in platinum content is cancelled out by the reduction in performance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grubb, W. T., and Michalske, C. J., J. Electrochem. Soc. 111, 1015 (1964).
Binder, H., Kohling, A., Krupp, H., Richter, K., and Sanstede, G., J. Electrochem. Soc., 112, 355 (1965).
Cairns, E. J., see p, 161 of this issue of Nature.
Thacker, R., presented at the 126th Electrochemical Society Meeting, Oct. 1964, see Extended Abst. of the Battery Div., 9, 22 (1964).
Niedrach, L. W. (unpublished results).
Niedrach, L. W., and Alford, H. R., J. Electrochem. Soc., 112, 117 (1965).
Taylor, W. F., Yates, D. J. C., and Sinfelt, J. H., J. Phys. Chem., 68, 2962 (1964).
Schwab, G. M., Block, J., and Schultze, D., Angew. Chem., 71, 101 (1959).
Gray, T. J., Masse, N. G., and Oswin, H. G., Paper No. 83, Paris Catalysis Conf. (1960).
Maxted, E. B., and Akhtar, S., J. Chem. Soc., 1995 (1960).
A part of the present work was cited previously; see White, E. R., and Maget, H. J. R., Proc Nineteenth Ann. Power Sources Conf., Atlantic City, N.J., May, 1965, p. 46.
Robell, A. J., Ballou, E. V., and Boudart, M., J. Phys. Chem., 68, 2748 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GRUBB, W., MCKEE, D. Boron Carbide, a New Substrate for Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts. Nature 210, 192–194 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/210192b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/210192b0
This article is cited by
-
Advanced Noncarbon Materials as Catalyst Supports and Non-noble Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells and Metal–Air Batteries
Electrochemical Energy Reviews (2021)
-
The dynamics of overlayer formation on catalyst nanoparticles and strong metal-support interaction
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Electronic metal-support interaction enhanced oxygen reduction activity and stability of boron carbide supported platinum
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Fuel cells: Problems and prospects
Proceedings / Indian Academy of Sciences (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.