Abstract
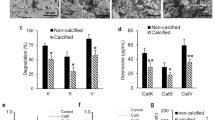
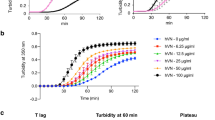
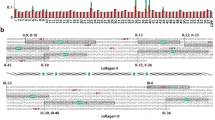
PREVIOUS publications from this laboratory have demonstrated that specific hydrated aliphatic aldehydes1,2 react both in vitro and in vivo3–5 with the freely rotatable nitrogen atoms6 of native and ‘purified’ collagen and elastin chains. The resulting products are highly cross-linked network structures7 which are characterized by ‘locking-in’ of dipoles8 normally present along the respective polypeptide chains. Unfortunately, little is known about the quantitative aspects of the involved reactions. The presently reported investigation was accordingly prompted, in which the binding of two specific C3 aldehydes to hide powder collagen, extracted aortic elastin, intact (control) bovine thoracic aortae and sonicated bovine thoracic aorta preparations were investigated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milch, R. A., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 93, 45 (1964).
Milch, R. A., and Murray, R. A., J. Amer. Leather Chemists' Assoc., 59, 310 (1964).
Milch, R. A., J. Amer. Leather Chemists' Assoc., 57, 581 (1962); Gerontologia, 7, 129 (1963); J. Surg. Res., 3, 254 (1963); J. Atheroscler. Res., 5, 215 (1965).
Milch, R. A., Jude, J. R., and Knaack, J., Surgery, 54, 104 (1963).
Kincaid, D. T., Baker, L. D., jun., and Milch, R. A., J. Surg. Res., 5, 120 (1965).
Milch, R. A., Nature, 205, 1108 (1965).
Milch, R. A., Gerontologia, 10, 117 (1965).
Milch, R. A., Frisco, L. J., and Szymkowiak, E. A., Biorheology (in, the press).
Hass, G. M., Arch. Path., 34, 971 (1942); Ayer, J. P., Hass, G. M., and Philpott, D. E., Arch. Path., 65, 519 (1958).
Milch, R. A., Gey, G. O., and Naughton, M. A., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 100, 623 (1965).
Clifford, R., and Karmen, A., submitted for publication.
Mendoza, S. A., and Milch, R. A., Surg. Forum, 15, 433 (1964).
Partridge, S. M., and Elsden, D. F., Biochem. J., 79, 26 (1961).
Anderson, B., Hoffman, P., and Meyer, K., J. Biol. Chem., 240, 156 (1965).
Gotte, L., Stern, P., Elsend, D. F., and Partridge, S. M., Biochem. J., 87, 344 (1963); Gotte, L., Serafini-Fracassini, A., and Moret, V., J. Atheroscler. Res., 3, 244 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MILCH, R., CLIFFORD, R. & MURRAY, R. Binding of Aliphatic Aldehydes to Collagen and Elastin Matrices. Nature 210, 1042–1043 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/2101042a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2101042a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.