Abstract
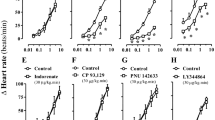
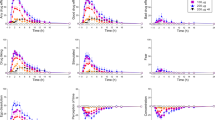
THE mechanism by which α-methyl-3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (methyldopa, Aldomet) lowers blood pressure in man has not been established definitely. While the inhibiting activity of the drug on decarboxylation of aromatic-L-amino-acids has been confirmed in human subjects and indeed was our reason for first studying the compound clinically1, it is doubtful that synthesis of the sympathetic transmitter, noradrenaline, is significantly affected by the drug. Thus, investigations in this laboratory and elsewhere2 have failed to show any decrease in the urinary excretion of the catecholamine metabolite, vanilmandelic acid, in patients receiving the drug. Furthermore, depletion of tissue-levels of noradrenaline by methyldopa and α-methyl-m-tyrosine in animals appears unrelated to the enzyme-inhibiting effects of these compounds3. Present evidence4,5 favours mediation of the depleting effect by amine metabolites formed by decarboxylation (to α-methyl-dopamine) and possibly subsequent β-hydroxylation (to α-methyl-noradrenaline).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oates, J. A., Gillespie, L., Udenfriend, S., and Sjoerdsma, A., Science, 131, 1890 (1960).
Cannon, P. J., Whitlock, R. T., Morris, R. C., Angers, M., and Laragh, J. H., J. Amer. Med. Assoc., 179, 673 (1962).
Hess, S. M., Connamacher, R. H., Ozaki, M., and Udenfriend, S., J. Pharm. Expt. Therap., 134, 129 (1961).
Udenfriend, S., Connamacher, R., and Hess, S. M., Biochem. Pharm., 8, 419 (1961).
Carlsson, A., and Lindquist, M., Acta Physiol. Scand., 54, 87 (1962).
Burn, J. H., and Rand, M. J., J. Physiol., 144, 314 (1958).
Pettinger, W., Spector, S., Horwitz, D., and Sjoerdsma, A. (in preparation).
Day, M. D., and Rand, M. J., J. Pharm. and Pharmacol., 15, 221 (1963).
Varma, D. R., and Benfey, B. G., J. Pharm. Expt. Therap., 141, 310 (1963).
Mueller, P. S., and Horwitz, D., J. Lipid Res., 3, 251 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PETTINGER, W., HORWITZ, D., SPECTOR, S. et al. Enhancement by Methyldopa of Tyramine Sensitivity in Man. Nature 200, 1107–1108 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/2001107a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2001107a0
This article is cited by
-
Influence of prenylamine on the cardiovascular effects of tyramine, noradrenaline and adrenaline in man
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (1971)
-
Tyramine pressor effects in man before and during treatment with nortriptyline or ECT: Correlation between plasma level and effect of nortriptyline
Pharmacologia Clinica (1970)
-
Orientierende Übersicht
Ergebnisse der Physiologie Biologischen Chemie und Experimentellen Pharmakologie (1966)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.