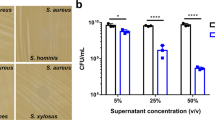
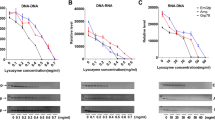
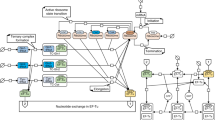
Abstract
IT has been established that chloramphenicol is a specific inhibitor of inducible enzyme formation and of protein synthesis in general1. The antibiotic does not exert its effect on protein synthesis by inhibition of amino-acid activation, by inhibition of peptide bond formation, or by inhibition of incorporation of amino-acids into cell-wall2. Pardee, Paigen and Prestidge3 reported that ribonucleic acid synthesized in the presence of chloramphenicol possessed an electrophoretic mobility which differed from that of normal ribonucleic acid synthesized in the absence of the antibiotic. It was later found by Neidhardt and Gros4 that this altered ribonucleic acid was unstable and was rapidly degraded in the absence of chloramphenicol. These observations have prompted the suggestion by Gale5 that “chloramphenicol alters, or in some way interferes with the function of the ribonucleic acid component concerned in amino-acid incorporation”.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gale, E. F., and Folkes, J. P., Biochem. J., 53, 493 (1953).
Mandelstam, J., and Roger, H. J., Nature, 181, 956 (1958).
Pardee, A. B., Paigen, K., and Prestidge, L. S., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 23, 162 (1957).
Neidhardt, F. C., and Gros, F., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 25, 513 (1957).
Gale, E. F., in “The Strategy of Chemotherapy” 8th Symp. Soc. Gen. Microbiol., ed. by S. T. Cowan and E. Rowatt (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1958).
Merkel, J. R., and Steers, E., J. Bact., 66, 389 (1953).
Kushner, D. J., Arch. Biochim. Biophys., 58, 347 (1955).
Ramsey, H. H., and Padron, J. L., Antibiotics and Chemother., 4, 537 (1955).
Ramsey, H. H., and Wilson, T. E., Nature, 180, 761 (1957).
Gale, E. F., and Folkes, J. P., Biochem. J., 59, 675 (1955).
Ben-Ishai, R., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 26, 477 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RAMSEY, H. Protein Synthesis as a Basis for Chloramphenicol-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus . Nature 182, 602–603 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/182602a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/182602a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.