Abstract
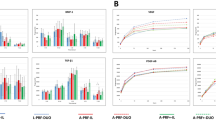
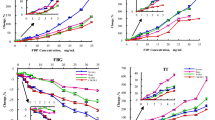
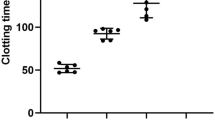
PLATELET-FREE, citrated plasma, collected and handled in silicone-treated apparatus, has a very long clotting time on recalcification. The exposure to glass surface greatly shortens the clotting time, and various hypotheses have been advanced to explain this phenomenon1–4. The present study is an attempt to examine certain aspects of this reaction by the exposure of various normal and pathological plasma specimens and plasma fractions to a standard glass surface in the form of glass ‘ballotini’ spheres of 0.12 mm. average diameter. The activity may be assessed either by recalcifying the activated specimen directly or by adding a sample to a standard volume of silicone-collected plasma and recording the re-calcified clotting time of the mixture. The use of this silicone plasma as a diluent is essential for testing samples which are devoid of one or more clotting factors (cf. Table 1). (For reasons to be discussed elsewhere, in some experiments ‘silicone plasma’ containing 2,000–10,000 platelets/c.mm. was used as the diluent for the activated, platelet-free samples.)
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conley, C. L., Hartmann, R. C., and Morse, W. L., J. Clin. Invest., 28, 340 (1949).
Tocantins, L. M., Amer. J. Physiol., 143, 67 (1945).
Fiala, S., Arch. Internal. Physiol., 58, 386 (1951).
Quick, A. J., Hussey, C. V., and Epstein, E., Amer. J. Physiol., 74, 123 (1951).
Biggs, R., Douglas, A. S., and Macfarlane, R. G., J. Physiol., 122, 538 (1953).
Dick, F. W., Jackson, D. P., and Conley, C. L., J. Clin. Invest., 33, 1423 (1954).
Armstrong, D., Keele, C. A., Jepson, J. B., and Stewart, J. W., Nature, 174, 791 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MARGOLIS, J. Glass Surface and Blood Coagulation. Nature 178, 805–806 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/178805b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/178805b0
This article is cited by
-
Synergistic Benefits on Combining Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Bone Graft Porous Particulate Materials
Biomedical Materials & Devices (2023)
-
Droplet Microfluidics with Reagent Micromixing for Investigating Intrinsic Platelet Functionality
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2021)
-
Acute cytotoxic effects of silica microparticles used for coating of plastic blood-collection tubes on human periosteal cells
Odontology (2020)
-
Direct activation of platelets by addition of CaCl2 leads coagulation of platelet-rich plasma
International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018)
-
The initiation and effects of plasma contact activation: an overview
International Journal of Hematology (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.