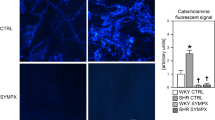
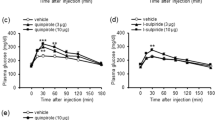
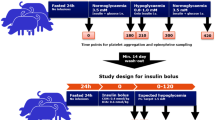
Abstract
IT is generally assumed that the stimulation of adrenalin secretion which is observed after insulin administration is a reaction not caused by insulin itself but by the hypoglycæmia which it produces. It has also often been claimed, with and without supporting evidence, that insulin hypoglycæmia is accompanied by hyperadrenalinæmia. This claim is not correct, as has recently been shown1. The intravenous injection of insulin in fasting subjects leads to an immediate and pronounced drop of the level of adrenergic amines in plasma which precedes the fall of the blood sugar. Likewise, in the recovery period, the return of the level of adrenergic amines to the norm precedes the rise of the blood sugar curve. If coma doses of insulin are injected the plasma-level of adrenergic amines remains depressed, until the coma is terminated by glucose administration. The effect of insulin is also observed, although in mild and modified form, if the development of hypoglycæmia is prevented by a preceding glucose ingestion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weil-Malherbe, H., and Bone, A. D., J. Ment. Sci., 98, 565 (1952); Biochem. J., 52, xi (1952). IIe Congrès Intern. Biochim., Résumés des Communications 67 (1952).
Weil-Malherbe, H., and Bone, A. D., Lancet, 264, 974 (1953).
Hökfelt, B., Acta Physiol. Scand., 25, suppl. 92 (1952).
Euler, U. S. von, and Luft, R., Metabolism, 1, 528 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WEIL-MALHERBE, H. Effect of Insulin on the Adrenergic Amines of Blood. Nature 172, 396–397 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1038/172396a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/172396a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.