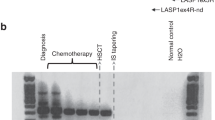
Summary:
Relapse is the major complication after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children. Since it has been possible to measure minimal residual disease (MRD) by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, this parameter is used more frequently in the treatment of ALL. In this article, the role of MRD and chimerism in the treatment and monitoring of pediatric transplantation recipients is described. Pre-SCT MRD levels can predict the risk of relapse and can thus be used to adjust treatment. Post-SCT MRD levels and changes in chimerism can predict relapses as well, although not many treatment options are available today, except relying on a graft-versus-leukemia effect mediated by graft-versus-host disease. Finding new treatments will be the challenge for the near future.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Dongen JJ, Seriu T, Panzer-Grumayer ER et al. Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood. Lancet 1998; 352: 1731–1738.
Knechtli CJ, Goulden NJ, Hancock JP et al. Minimal residual disease status before allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is an important determinant of successful outcome for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1998a; 92: 4072–4079.
Goulden N, Bader P, van-der-Velden VHJ et al. Minimal residual disease prior to stem cell transplant for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 24–29.
Krejci O, van-der-Velden VHJ, Bader P et al. Level of minimal residual disease prior to haematopoietic stem cell transplantation predicts prognosis in paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a report of the Pre-BMT MRD Study Group. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 849–851.
Bruggemann M, van-der-Velden VHJ, Raff T et al. Rearranged T-cell receptor beta genes represent powerful targets for quantification of minimal residual disease in childhood and adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 709–719.
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Seriu T, Stolz F et al. Primers and protocols for standardized detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene rearrangements and TAL1 deletions as PCR targets: report of the BIOMED-1 CONCERTED ACTION: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Leukemia 1999; 13: 110–118.
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Verhagen OJ, Tibbe GJ et al. Real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using junctional region specific TaqMan probes. Leukemia 1998; 12: 2006–2014.
van-der-Velden VHJ, Wijkhuijs JM, Jacobs DC et al. T cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements as targets for detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Leukemia 2002b; 16: 1372–1380.
Knechtli CJ, Goulden NJ, Hancock JP et al. Minimal residual disease status as a predictor of relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1998b; 102: 860–871.
van-der-Velden VHJ, Jacobs DC, Wijkhuijs AJ et al. Minimal residual disease levels in bone marrow and peripheral blood are comparable in children with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), but not in precursor-B-ALL. Leukemia 2002a; 16: 1432–1436.
Bader P, Beck J, Frey A et al. Serial and quantitative analysis of mixed hematopoietic chimerism by PCR in patients with acute leukemias allows the prediction of relapse after allogeneic BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 487–495.
Bader P, Holle W, Klingebiel T et al. Mixed hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: the impact of quantitative PCR analysis for prediction of relapse and graft rejection in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 697–702.
Goulmy E . Minor histocompatibility antigens: allo target molecules for tumor-specific immunotherapy. Cancer J 2004; 10: 1–7.
Bader P, Kreyenberg H, Hoelle W et al. Increasing mixed chimerism is an important prognostic factor for unfavorable outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation: possible role for pre-emptive immunotherapy? J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1696–1705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilham, M., Balduzzi, A., Bader, P. et al. Is there a role for minimal residual disease levels in the treatment of ALL patients who receive allogeneic stem cells?. Bone Marrow Transplant 35 (Suppl 1), S49–S52 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704847
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704847
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Delayed lymphocyte infusion in children given SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Allogeneic transplantation for childhood ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
B-cell reconstitution after allogeneic SCT impairs minimal residual disease monitoring in children with ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Treatment options for the management of acute leukaemia relapsing following an allogeneic transplant
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)