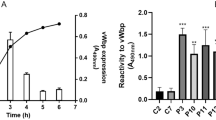
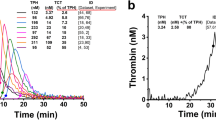
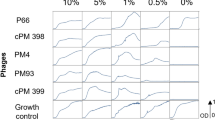
Abstract
IN 1944, Smith and Hale1 showed that the clotting of fibrinogen by coagulase depends on an activator present in the plasma of certain animals, notably humans and rabbits. Since a fibrinogen–prothrombin complex prepared from human plasma by Mellanby's2 acid precipitation method, which could be clotted by tissue kinase, could not be clotted by coagulase, they concluded that the activator was not prothrombin. Later, Tager3 and Tager and Hales4 noted certain resemblances between the physical properties of activator and prothrombin, both being precipitated with the globulin fractions in the region of pH 5.0 and by 50 per cent saturation with ammonium sulphate. In ethanol-precipitated fractions of plasma prepared by the method of Cohn5, activator was present in fractions III-1, III-2 and IV-1, whereas prothrombin is believed to occur only in III-2. Both prothrombin and activator were absorbed from plasma by barium sulphate; but considerable dissociation followed repeated Seitz filtration of human plasma, prothrombin activity being lost without comparable loss of activator. Studies by Kaplan and Spink6 disagreed with these findings, inasmuch as they found activator to be associated with the albumin fraction in ammonium sulphate fractionation, and to lie mainly in IV-4 of the ethanol precipitate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, W., and Hale, J. H., Brit. J. Exp. Path., 25, 101 (1944).
Mellanby, J., J. Physiol., 38, 28 (1908).
Tager, M., Yale J. Biol. Med., 20, 369 (1948).
Tager, M., and Hales, H. B., J. Immunol., 60, 1 (1948).
Cohn, E. J., Ann. Inter. Med., 26, 341 (1947).
Kaplan, M. H., and Spink, W. W., Blood, 3, 573 (1948).
Quick, A. J., “The Hæmorrhagic Diseases” (Springfield, Illinois: C. C. Thomas, 1942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DUTHIE, E., LORENZ, L. Staphylococcal Coagulase: the Nature of Plasma Activator in the Clotting Process. Nature 165, 729–730 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165729b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/165729b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.