Abstract
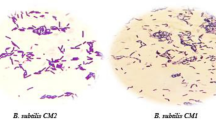
During the course of an investigation on the rate of growth of Str. lactis in raw and heated milk, it was found that the rate of growth as estimated by the colony count test at 37° C. was very much greater in heated milk (milk heated to 70° C. for one hour), but that the reduction of methylene blue and resazurin was the same, in spite of this apparent greater metabolic activity of the organisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hobbs, B. C., J. Dairy Res., 10, 49 (1939).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MORRIS, C., EDWARDS, M. Limitations of the Colony Count Test for Assessing the Total Number of Viable Bacteria in Raw and Heated Milk. Nature 160, 434–435 (1947). https://doi.org/10.1038/160434b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/160434b0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.