Abstract
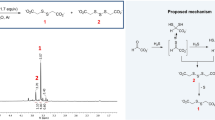
WE have previously demonstrated that thiamin pyrophosphate may be synthesized from the free vitamin by the action of enzymes present in alkaline washed brewer's bottom yeast, provided that hexose-diphosphate and certain factors present in boiled aqueous extracts of animal tissues are present1,3. Synthesis under these conditions was completely inhibited by 0·005 M. sodium iodoacetate, but was relatively unaffected by 0·04 M. sodium fluoride. More recently3, we have demonstrated that cozymase and acetaldehyde may be substituted for the boiled tissue extract with no change in the degree of synthesis or of the iodoacetate inhibition. Phosphoglyceric acid may also be substituted for the boiled tissue extract, but under these conditions iodoacetate fails to affect the synthesis while fluoride causes complete inhibition3. Using specially prepared alkaline washed yeast, we have found that cocarboxylase synthesis with phosphoglyceric acid is considerably diminished. It may be restored, however, by the addition of catalytic quantities of adenylic acid. As a result of these experiments we have proposed the reaction
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipschitz, M. A., Potter, V. R., and Elvehjem, C. A., Biochem. J., 32, 474 (1938).
Lipschitz, M. A., Potter, V. R., and Elvehjem, C. A., J. Biol. Chem., 124, 147 (1938).
Lipton, M. A., and Elvehjem, C. A., Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quant. Biology, 7 (1939).
Weil-Malherbe, H., Chem. Ind., 58, 1021 (1939).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LIPTON, M., ELVEHJEM, C. Mechanism of the Enzymatic Phosphorylation of Thiamin. Nature 145, 226–227 (1940). https://doi.org/10.1038/145226c0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/145226c0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.